1
2
3
4
| public interface MemberRepository extends JpaRepository<Member, Long> {
List<Member> findByUsername(String username);
}
|
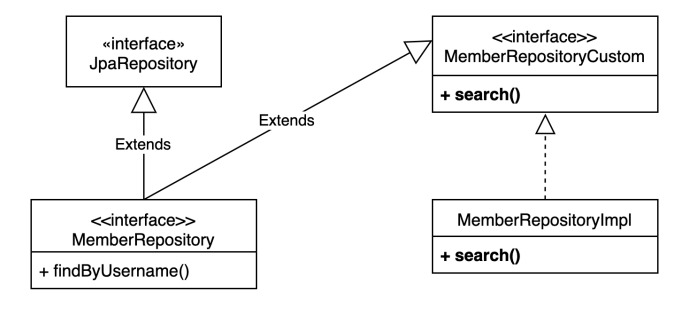
문제는 Querydsl로 search를 작성할 수 없다.
따라서 사용자 정의 리포지토리가 필요하다.
사용자 정의 리포지토리
- 사용자 정의 인터페이스 작성
- 사용자 정의 인터페이스 구현
- 스프링 데이터 리포지토리에 사용자 정의 인터페이스 상속
1
2
3
4
| public interface MemberRepositoryCustom {
List<MemberTeamDto> search(MemberSearchCondition condition);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| public class MemberRepositoryImpl implements MemberRepositoryCustom {
private final JPAQueryFactory queryFactory;
public MemberRepositoryImpl(EntityManager em) {
this.queryFactory = new JPAQueryFactory(em);
}
@Override
public List<MemberTeamDto> search(MemberSearchCondition condition) {
return queryFactory
.select(new QMemberTeamDto(
member.id,
member.username,
member.age,
team.id,
team.name
))
.from(member)
.leftJoin(member.team, team)
.where(usernameEq(condition.getUsername()),
teamNameEq(condition.getTeamName()),
ageGoe(condition.getAgeGoe()),
ageLoe(condition.getAgeLoe()
))
.fetch();
}
private BooleanExpression usernameEq(String username) {
return StringUtils.hasText(username) ? null : member.username.eq(username);
}
private BooleanExpression teamNameEq(String teamName) {
return StringUtils.hasText(teamName) ? null : team.name.eq(teamName);
}
private BooleanExpression ageGoe(Integer ageGoe) {
return ageGoe == null ? null : member.age.goe(ageGoe);
}
private BooleanExpression ageLoe(Integer ageLoe) {
return ageLoe == null ? null : member.age.loe(ageLoe);
}
}
|
그리고 MemberRepository에 MemberRepositoryCustom을 상속해주면 된다.
스프링 데이터 페이징 활용
- 스프링 데이터의 Page, Pageable을 활용한다.
- 전체 카운트를 한 번에 조회하는 단순한 방법
- 데이터 내용과 전체 카운트를 별도로 조회하는 방법
Querydsl 페이징 연동
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public interface MemberRepositoryCustom {
List<MemberTeamDto> search(MemberSearchCondition condition);
Page<MemberTeamDto> searchPageSimple(MemberSearchCondition condition, Pageable pageable);
Page<MemberTeamDto> searchPageComplex(MemberSearchCondition condition, Pageable pageable);
}
|
전체 카운트를 한 번에 조회하는 단순한 방법
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| @Override
public Page<MemberTeamDto> searchPageSimple(MemberSearchCondition condition,
Pageable pageable) {
QueryResults<MemberTeamDto> results = queryFactory
.select(new QMemberTeamDto(
member.id,
member.username,
member.age,
team.id,
team.name))
.from(member)
.leftJoin(member.team, team)
.where(usernameEq(condition.getUsername()),
teamNameEq(condition.getTeamName()),
ageGoe(condition.getAgeGoe()),
ageLoe(condition.getAgeLoe()))
.offset(pageable.getOffset())
.limit(pageable.getPageSize())
.fetchResults();
List<MemberTeamDto> content = results.getResults();
long total = results.getTotal();
return new PageImpl<>(content, pageable, total);
}
|
- Querydsl이 제공하는 fetchResults()를 사용해 Content와 전체 카운트를 한 번에 조회할 수 있다.
데이터 내용과 전체 카운트를 별도 조회
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| @Override
public Page<MemberTeamDto> searchPageComplex(MemberSearchCondition condition,
Pageable pageable) {
List<MemberTeamDto> content = queryFactory
.select(new QMemberTeamDto(
member.id,
member.username,
member.age,
team.id,
team.name))
.from(member)
.leftJoin(member.team, team)
.where(usernameEq(condition.getUsername()),
teamNameEq(condition.getTeamName()),
ageGoe(condition.getAgeGoe()),
ageLoe(condition.getAgeLoe()))
.offset(pageable.getOffset())
.limit(pageable.getPageSize())
.fetch();
long total = queryFactory
.select(member)
.from(member)
.leftJoin(member.team, team)
.where(usernameEq(condition.getUsername()),
teamNameEq(condition.getTeamName()),
ageGoe(condition.getAgeGoe()),
ageLoe(condition.getAgeLoe()))
.fetchCount();
return new PageImpl<>(content, pageable, total);
}
|
- 전체 카운트를 조회하는 방법을 최적화 할 수 있다면 이런식으로 분리하면 된다.
- 코드를 리팩토링해 내용 쿼리와 전체 카운트 쿼리를 읽기 좋게 분리하면 좋다.
CountQuery 최적화
때에 따라 아래의 카운트 쿼리 부분을 생략할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| long total = queryFactory
.select(member)
.from(member)
.leftJoin(member.team, team)
.where(usernameEq(condition.getUsername()),
teamNameEq(condition.getTeamName()),
ageGoe(condition.getAgeGoe()),
ageLoe(condition.getAgeLoe()))
.fetchCount();
|
- 페이지 시작이면서 컨텐츠 사이즈가 페이지 사이즈보다 작을 때
- 마지막 페이지 일 때. (offset + 컨텐츠 사이즈를 더해 전체 사이즈를 구한다.)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| JPAQuery<Member> countQuery = queryFactory
.select(member)
.from(member)
.leftJoin(member.team, team)
.where(usernameEq(condition.getUsername()),
teamNameEq(condition.getTeamName()),
ageGoe(condition.getAgeGoe()),
ageLoe(condition.getAgeLoe()
));
return PageableExecutionUtils.getPage(content, pageable, countQuery::fetchCount);
|
- 스프링 데이터 라이브러리가 제공하는 약간의 최적화 방법이다.
컨트롤러 활용
1
2
3
4
| @GetMapping("/api/members")
public List<MemberTeamDto> searchMember(MemberSarchCondition condition, Pageable pageable) {
return memberRepository.searchPageSimple(condition, pageable);
}
|