이제 코드로 JDBC를 어떻게 사용하는지 알아본다.
H2 DB와 연결
1
2
3
4
5
public abstract class ConnectionConst {
public static final String URL = "jdbc:h2:tcp://localhost/~/test2";
public static final String USERNAME = "sa";
public static final String PASSWORD = "";
}
DB를 연결하기 위한 정보들을 상수로 관리하는 추상클래스를 만든다. (객체로 생성 X)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
@Slf4j
public class DBConnectionUtil {
public static Connection getConnection() {
try {
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USERNAME, PASSWORD);
log.info("get connection={}, class={}", connection, connection.getClass());
return connection;
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
}
}
}
( ConnectionConst는 static import를 해주어 URL, USERNAME, PASSWORD로 사용 )
데이터베이스에 연결하려면 JDBC가 제공하는 DriverManager.getConnection()을 사용하면 된다. 라이브러리에 있는 데이터베이스 드라이버를 찾아 해당 드라이버가 제공하는 커넥션을 반환해준다.
여기서는 H2 데이터베이스 드라이버가 작동해 실제 데이터베이스와 커넥션을 맺고 그 결과를 반환해준다.
test
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
class DBConnectionUtilTest {
@Test
void connection() {
Connection connection = DBConnectionUtil.getConnection();
assertThat(connection).isNotNull();
}
}
1
[main] INFO hello.jdbc.connection.DBConnectionUtil -- get connection=conn0: url=jdbc:h2:tcp://localhost/~/test2 user=SA, class=class org.h2.jdbc.JdbcConnection
테스트가 성공하고 위와 같은 DBConnecionUtil에서 남긴 로그를 볼 수 있다.
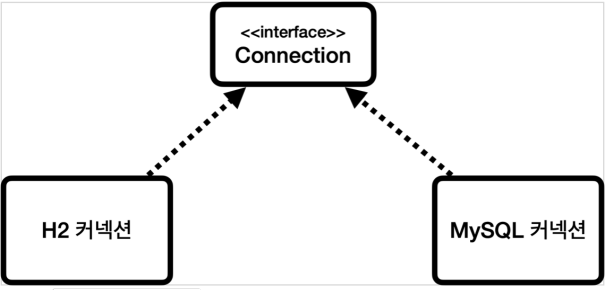
class=class org.h2.jdbc.JdbcConnection 을 볼 수 있고, 이는 H2 데이터베이스 드라이버가 제공하는 H2 전용 커넥션이다. 이 커넥션은 당연히 JDBC 표준 커넥션 인터페이스인 java.sql.Connection 인터페이스를 구현한 것이다.
JDBC DriverManager
JDBC는 java.sql.Connection 표준 커넥션 인터페이스를 정의하고, H2 데이터 베이스 드라이버는 인터페이스의 구현체인 org.h2.jdbc.JdbcConnection 구현체를 제공한다.
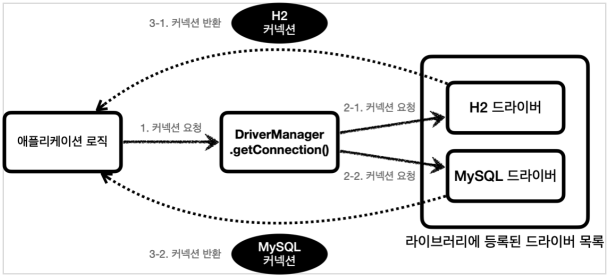
JDBC가 제공하는 DriverManager는 라이브러리에 등록된 DB 드라이버들을 관리하고, 커넥션을 획득하는 기능을 제공한다.
- 애플리케이션 로직에서 커넥션이 필요하면 DriverManager.getConnection()을 호출한다.
- DriverManager는 라이브러리에 등록된 드라이버 목록을 자동으로 인식한다. 이 드라이버들에게 순서대로 다음 정보를 넘겨 커넥션을 획득할 수 있는지 확인한다.
- 찾은 커넥션 구현체가 클라이언트에 반환된다.
커넥션 획득 과정
- URL 확인
- 이름 비밀번호 등 접속에 필요한 추가 정보 확인
- 각각의 드라이버는 URL 정보를 체크해서 본인이 처리할 수 있는 요청인지 확인한다. 예를 들어 URL이 jdbc:h2로 시작하면 이것은 h2 데이터베이스에 접근하기 위한 규칙이다. 따라서 H2 드라이버는 본인이 처리할 수 있으므로 실제 DB에 연결해 커넥션을 획득하고 이 커넥션을 클라이언트에 반환한다.
- 만약 본인이 처리할 수 없다는 결과를 반환하게 되면 다음 드라이버로 순서가 넘어간다. (ex - URL이 jdbc:h2인데 드라이버는 MySQL)
JDBC 활용
JDBC를 사용해 회원(Member) 데이터를 데이터베이스에 관리하는 기능을 만들어본다.
주의
member 테이블을 미리 만들어두어야 한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
drop table member if exists cascade;
create table member (
member_id varchar(10),
money integer not null default 0,
primary key (member_id)
);
등록
Member
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
@Data
public class Member {
private String memberId;
private int money;
public Member() {
}
public Member(String memberId, int money) {
this.memberId = memberId;
this.money = money;
}
}
MemberRepository
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
@Slf4j
public class MemberRepositoryV0 {
public Member save(Member member) throws SQLException {
String sql = "insert into member(member_id, money) values (?, ?)";
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try {
con = getConnection();
pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, member.getMemberId());
pstmt.setInt(2, member.getMoney());
pstmt.excuteUpdate();
return member;
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.error("db error", e);
throw e;
} finally {
close(con, pstmt, null);
}
}
private void close(Connection con, Statement stmt, ResultSet rs) {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.info("error", e);
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.info("error", e);
}
}
if (con != null) {
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.info("error", e);
}
}
}
private Connection getConnection() {
return DBConnectionUtil.getConnection();
}
}
- getConnection(): DBConnectionUtil를 통해 DB 커넥션 획득
- sql: 데이터베이스에 전달할 SQL을 정의한다.
- 데이터 등록을 위해 insert sql을 정의했다.
- con.prepareStatement(sql): 데이터베이스에 전달할 SQL과 파라미터로 전달할 데이터들을 준비한다.
- pstmt.setString(1, member.getMemberId()): SQL의 첫번째 ?에 값을 지정한다. 문자이므로 setString을 사용한다.
- pstmt.setInt(2, member.getMoney()): SQL의 두번째 ?에 값을 지정한다.
- pstmt.executeUpdate(): Statement를 통해 준비된 SQL을 커넥션을 통해 실제 데이터베이스에 전달한다.
- 참고로 executeUpdate()는 int를 반환하는데 영향받은 DB row 수를 반환한다.
- 여기서는 1을 반환. (영향받은 row = 1)
리소스 정리
쿼리를 실행하고 나면 리소스를 정리해야 한다. 여기서는 리소스로 Connection, PreparedStatement를 사용했다. 리소스 정리는 항상 역순으로 해야한다.
Connection을 먼저 획득하고 Connection을 통해 PreparedStatement를 만들었기 때문에 반환할때는 pstmt.close() -> con.close() 순 인 것이다.
참고로 여기서 사용하지 않은 ResultSet을 반환하는데 이는 결과를 조회할 때 사용한다.
주의
리소스 정리는 반드시 해야한다. 따라서 예외가 발생하든 하지 않든 항상 수행되어야 하므로 finally 구문에 주의해 작성해야 한다.
이 부분을 놓치게 되면 커넥션이 끊어지지 않고 계속 유지될 수 있다. 이런 것을 리소스 누수라고 하는데 결과적으로 커넥션 부족으로 장애가 발생할 수 있다.
참고
PreparedStatement는 Statement의 자식타입이다. ?를 통한 파라미터 바인딩을 가능하게 해준다. SQL Injection 공격 (유튜브 영상에서 봄 - 간단히 어떤 입력에 쿼리를 넣어 DB에 접근) 을 예방하기 위해 필요하다.
조회
MemberRepository 추가
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
public Member findById(String memberId) throws SQLException {
String sql = "select * from member where member_id = ?";
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
con = getConnection();
pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, memberId);
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
Member member = new Member();
member.setMemberId(rs.getString("member_id"));
member.setMoney(rs.getInt("money"));
return member;
} else {
throw new NoSuchElementException("member not found memberId=" + memberId);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.error("db error", e);
throw e;
} finally {
close(con, pstmt, rs);
}
}
- rs = pstmt.executeQuery(): 데이터를 변경할 때는 executeUpdate()를 사용하지만, 데이터를 조회할 때는 executeQuery()를 사용한다. 결과를 ResultSet에 담아 반환한다.
- ResultSet
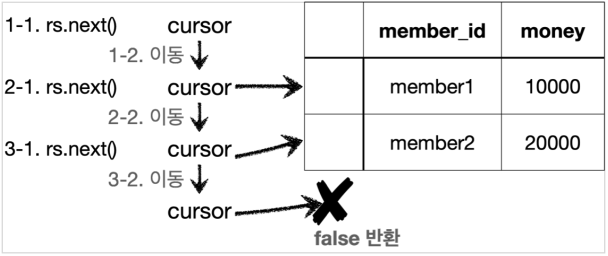
- 보통 select 쿼리의 결과가 순서대로 들어간다.
- 예를 들어 select member_id, money 라고 지정하면 member_id, money라는 이름으로 데이터가 저장된다.
- ResultSet 내부에 있는 Cursor를 이동해 다음 데이터를 조회할 수 있다.
- rs.next(): 커서가 다음으로 이동한다. 최초의 커서는 데이터를 가리키고 있지 않아 rs.next()를 한번은 호출해야 데이터를 조회할 수 있다. true, false로 데이터의 유무를 반환한다.
- rs.getString(“member_id”): 현재 커서가 가리키고 있는 위치의 member_id 데이터를 String 타입으로 반환한다.
- rs.getInt(“money”): 현재 커서가 가리키고 있는 위치의 money 데이터.
- 보통 select 쿼리의 결과가 순서대로 들어간다.
findById()에서는 회원 하나를 조회하는 것이 목적이기 때문에 조회 결과가 항상 1건이다. 따라서 while 대신 if를 사용하게 된다. (where member_id)
수정, 삭제
등록과 비슷하다. 등록과 수정, 삭제처럼 데이터를 변경하는 쿼리는 executeUpdate()를 사용하면 된다.
MemberRepository 추가
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
public void update(String memberId, int money) throws SQLException {
String sql = "update member set money=? where member_id=?";
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try {
con = getConnection();
pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setInt(1, money);
pstmt.setString(2, memberId);
int resultSize = pstmt.executeUpdate();
log.info("resultSize={}", resultSize);
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.error("db error", e);
throw e;
} finally {
close(con, pstmt, null);
}
}
public void delete(String memberId) throws SQLException {
String sql = "delete from member where member_id=?";
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try {
con = getConnection();
pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, memberId);
pstmt.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.error("db error", e);
throw e;
} finally {
close(con, pstmt, null);
}
}
참고
테스트를 할 때 DB에 연동되기 때문에 데이터가 저장됨에 따라 테스트에 오류가 발생할 수 있다. 예를 들어 테스트를 두 번 수행하면 이미 데이터를 삭제했는데 또 그 데이터를 삭제하는 로직을 테스트하는 것이다. (코드가 같기 때문)
이런 문제는 트랜잭션을 활용하면 해결할 수 있다.