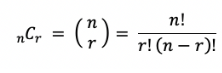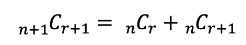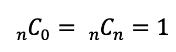브루트 포스(완전탐색)
- 선형 구조 : 순차 탐색
- 비선형 구조 : 백트래킹, DFS, BFS
완전탐색할 경우 시간복잡도로 계산되는 최댓값이 1억을 넘지 않으면 사용 가능.
정렬
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Arrays.sort(arr); // O(n^2)
Arrays.sort(arr, Collections.reverseOrder()); // 내림차순
Collections.sort(arr); // O(n) ~ O(nlogn)
모든 수를 정렬해서 출력하라 했을 때
for문으로 System.out.println() 쓰면 안되는 경우 있음.
이때는 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(arr.get(i)).append("\n");
System.out.print(sb);
- 카운팅정렬 O(n + k)
데이터의 값이 몇 번 나왔는지 세어주고 그 값을 이용한 정렬.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
class Main
{
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception
{
int[] cnt = new int[10001];
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
cnt[Integer.parseInt(br.readLine())]++;
}
//cnt[index] 에서 index에 해당하는 값의 개수가 담겨있는 배열이 됨.
//class를 만들어 객체에 value, index를 저장해 Arrays.sort 이용하여 정렬 가능.
}
}
- Comparable(CompareTo), Arrays.sort(Comparator) - 재정의
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
class Main
{
static class Point implements Comparable<Point>
{
private int x,y;
Point(int x, int y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Point p)
{
if(this.x == p.x)
{
return this.y - p.y;
}
return this.x - p.x;
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception
{
List<Point> points = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
points.add(new Point(x,y));
}
Collections.sort(points);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
class Main
{
static class Point
{
private int x,y;
Point(int x, int y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception
{
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
point[i] = new Point(x,y);
}
Arrays.sort(point, new Comparator<Point>() {
@Override
public int compare(Point p1, Point p2)
{
if(p1.x == p2.x)
{
return p1.y - p2.y;
}
else
{
return p1.x - p2.x;
}
}
}); //x값을 오름차순으로 정렬하고 만약 x값이 같다면 y값기준 오름차순으로.
}
}
Comparable 상속 -> compareTo (클래스 내 함수이름)
new Comparator<>() -> compare (sort 재정의 함수 이름)
**Collections.sort(a,new Comparator<>()) 일 때 a에 set 안됨. list로 변환해 사용.
- 람다식 이용
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>();
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
set.add(br.readLine());
}
List<String> setToList = new ArrayList<>(set);
Collections.sort(setToList, (s1,s2)->{
return s1.length() - s2.length();
}); //String의 길이로 먼저 정렬 한 후
Collections.sort(setToList, (s1,s2)->{
if(s1.length() == s2.length())
{
return s1.compareTo(s2);
}
else {
return s1.length() - s2.length();
}
}); // 길이가 같다면 사전순, 아니라면 길이순 정렬.
- HashMap을 이용한 정렬
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
HashMap<String, Integer> word_map = new HashMap<>(); // 단어, 빈도수
word_map.put(str, word_map.getOrDefault(str, 0) + 1);
List<String> words = new ArrayList<>(word_map.keySet()); // key들을 list로.
Collctions.sort(words, (s1, s2) -> {
int c1 = word_map.get(s1); //단어가 나온 횟수
int c2 = word_map.get(s2);
if(c1 == c2)
{
if(s1.length() == s2.length())
{
return s1.compareTo(s2); //3순위. 사전순
}
return s2.length() - s1.length(); //2순위. 길이가 긴 순
}
return c2-c1; //1순위. 빈도수 내림차순.
});
Collections.binarySearch(collection, key)
해당 컬렉션에서 key에 해당하는 값이 존재하면 일치하는 index를 반환한다.
없다면 0 이하의 수가 출력된다.
sort후 binarySearch를 이용하면 탐색 시간을 많이 줄일 수 있다.
- BinarySearch 직접구현 응용 (lowerbound, upperbound)
중복된 원소가 있을 때 기존의 binarySearch는 첫번째 원소를 찾음(lowerbound)
따라서 중복된 원소의 끝부분을 찾고싶거나 개수를 알고싶을 때 upperbound 이용.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
private static int lowerbound(int[] arr, int key)
{
int start = 0;
int end = arr.length;
while(start < end)
{
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if(key <= arr[mid])
{
end = mid; // end를 start쪽으로 당겨야함. 따라서 같을때 end=mid;
}
else start = mid+1;
}
return start;
}
private static int upperbound(int[] arr, int key)
{
int start = 0;
int end = arr.length;
while(start < end)
{
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if(key < arr[mid])
{
end = mid;
}
else start = mid + 1; //start를 end쪽으로 당겨야함.
}
return start;
}
최대공약수(gcd), 최소공배수(lcd)
- 최대공약수 - 큰 수 / 작은수 떨어질 때 작은수 or 작은수 / 나머지 반복
- 최소공배수 - 수 * 수 / gcd
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public static int gcd(int a, int b){ // (a > b)
if(a % b == 0) return b;
return gcd(b, a%b);
}
public static int lcm(int a, int b, int gcd)
{
return a*b / gcd;
} // 기억안나면 for문 i*i 이용해서 둘 다 나머지 0일때 나누는 방식 사용 가능.
소수 구하기
- 에라토스테네스의 체
2부터 n까지의 숫자중에서 에라토스테네스의 체로 소수를 찾으려면, 2부터 시작해 n까지의 자연수를 차례로 쓴다. (2, 3, 4, 5… n)
그리고 2 이외의 2의 배수를 지운다. 이 때 2가 최초의 소수가 된다.
그 다음 소수인 3을 제외한 3의 배수를 지운다.
이 방법을 다음에 지울 소수, 즉 p의 제곱이 n보다 커질 때까지 이 방법을 계속한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
private void setPrime(){
prime[0] = true;
prime[1] = true;
for(int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(n); i++)
{
for(int j = i*i; j < n; j+=i) // i*i -> i를 제외한 j+=i -> i의 배수를 지우겠다.
{
if(prime[j] == false) prime[j] = true; // true이면 소수가 아닌 수.
}
}
- 소수 판별
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
private boolean isPrime(int n) {
if(n <= 1) return false;
for (int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(n); i++) // (<=)
{
if (n % i == 0)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
- BigInteger 이용
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
improt java.math.BigInteger;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
long num = Long.parseLong(br.readLine()l
BigInteger bi = new BigInteger(String.valueOf(num));
bi.isProbablePrime(10); // bi의 수가 소수인지 판별 (10은 정확도?) t/f
bi.nextProbablePrime(); // bi의 수보다 큰 다음 소수 출력
}
}
조합
위와 같은 공식으로 n개 중 r개 고르는 경우의 수를 구할 수 있다.
팩토리얼로도 구할 수 있지만
조합은 이러한 성질을 가지므로
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
dp[31][31] // 조합값을 저장해 이미 계산한 조합은 또 계산하는 일이 없도록.
private static int C(int N, int R){
if(N == R || K == 1) dp[N][R] = 1;
if(dp[N][R] > 0) return dp[N][R];
dp[N][R] = C(N-1, R-1) + C(N-1, R);
return dp[N][R];
}
재귀함수를 통해 효율적으로 값을 구할 수 있다.
최빈값 구하기(HashMap, 카운팅정렬)
- HashMap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
//list의 숫자들 중 가장 많이 나온 값 구하기.
for(int num : list)
{
map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
// key값에 num,
map.getOrDefault(num, 0)은 해당 key값에 num이 있다면 해당 key값에 대응하는 value값에 1을 더해서 다시 넣어주는 것이고
없다면 0을 리턴하고 거기에 0+1을 해서 넣어주는 것.
}
int max_count = 0;
for(int value: map.values())
{
max_count = Math.max(number, value);
//가장 많이 나온 수를 구함. (map value의 max값)
}
for(int key : map.keySet())
{
if(map.get(key) == max_count) //key의 value값이 max_count와 같다
{
list.add(key); //list에 해당 key값을 넣는다.
}
} //list내에 최빈값이 동일한 수들이 담겨있다.
- 카운팅정렬
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
count[value]++;
int counting = 0;
int mode_max = 0; //최빈값의 최대.
boolean flag = false; // 최대인 최빈값이 여러개일 때 2번째로 작은수를 구하기위함.
for(int i = min; i <= max; i++)
{
if(count[i] > 0)
{
if(counting <= N / 2) //중앙값 구하기
{
counting += count[i]; // 누적값(counting)이 중앙index에 다다를때 까지 counting을 계속 누적시킴.
median = i; // 다다랐을 때 i값이 중앙값.
}
if(mode_max < arr[i])
{
mode_max = arr[i];
mode = i;
flag = true;
}
else if(mode_max == arr[i] && flag)
{
mode = i;
flag = false;
}
}
}
재귀 응용 - 하노이의 탑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
static void hanoi(int size, int start, int mid, int to)
{
if(size == 1) // 이동해야 할 원판이 한개일 때
{
System.out.println(start + " " + to);
cnt++;
return;
}
hanoi(size - 1, start, to, mid);
//size - 1개의 원판을 start지점에서 to를 거쳐 mid지점으로 옮긴다.
System.out.println(start + " " to);
cnt++;
hanoi(size - 1, mid, start, to);
//mid 지점의 원판을 start를 거쳐 to지점으로 옮긴다.
}
size가 1이 될때까지 출력되는 것은 아무것도 없이 hanoi(size - 1, start, to, mid) 함수가 호출되는데
mid, to가 계속 바뀌면서 size가 홀수일때는 옮기는 첫 원판의 목적지가 to가 되고 짝수일때는 첫 원판의 목적지가 mid가 된다.
size가 1이되면 출력 후 return하고 size가 2인 함수로 다시 되돌아가 첫 원판을 옮기고 남은 원판 하나를 첫 원판의 목적지와 다른 mid에 놓게 된다.
(System.out.println(start + “ “ + to);)
**size 1일때 함수의 to와 size 2일때 함수의 to는 다르다.
이후 mid의 원판을 start를 거쳐 to로 옮기게 되는데 size 2에서의 함수를 따라가보면 바로 위에서 옮긴 원판(System.out.println(start + “ “ + to);)가 아닌 이미 옮긴 다른 원판을 옮기게 된다.